Introduction: Why ViDA Demands a New Approach to VAT Validation
The VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) initiative marks a fundamental shift in how businesses across the EU — and those trading with the EU — must manage VAT compliance. Introduced by the European Commission, ViDA sets out to modernize the VAT system through mandatory e-invoicing, real-time digital reporting, and increased platform liability, with implementation phases starting as early as 2028.
These changes are not just technical adjustments — they redefine how VAT compliance must be handled operationally. Businesses will need to ensure that every VAT number they collect, process, or reference is accurate, up to date, and verifiable against official government records. Failure to do so could result in invoice rejections, regulatory penalties, or exposure to tax audits.
For companies still relying on fragmented tools like VIES, static spreadsheets, or manual checks, ViDA will make those methods obsolete.
Understanding the Core ViDA Reforms
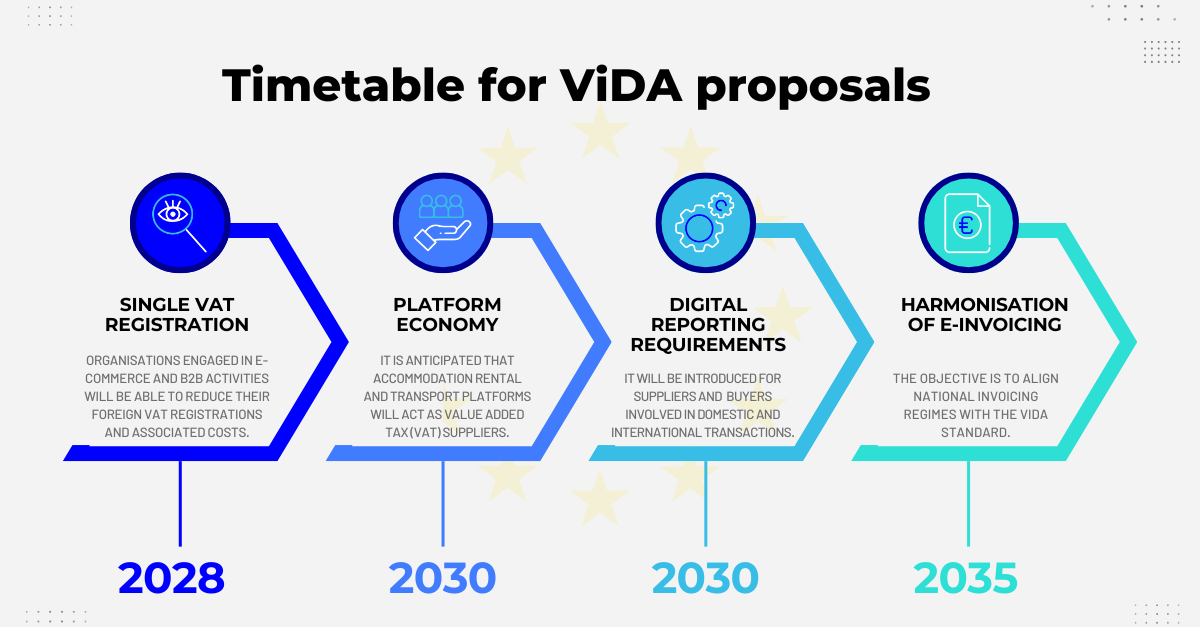
The VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) proposal, introduced by the European Commission, is designed to modernize how VAT is administered across the EU. It consists of three main pillars that will have far-reaching implications for how businesses validate, report, and manage VAT-related data:
1. Digital Reporting Requirements (DRR)
Starting from 2028, businesses engaged in intra-EU B2B transactions will be required to submit invoice data in near real-time to tax authorities. This replaces traditional VAT returns and introduces:
- A harmonized digital reporting format across EU member states
- Mandatory submission of structured electronic invoices within 2 days of issuance
- Increased scrutiny and reduced tolerance for errors in VAT numbers and entity data
| Implication: Businesses will need automated systems to validate VAT numbers before issuing invoices. Delays or mismatches will lead to reporting failures and financial exposure.
2. Mandatory E-Invoicing
ViDA will make e-invoicing the default method for cross-border B2B transactions within the EU. Unlike current systems where e-invoicing is optional or varies by country, the new rules will:
- Require structured invoice formats aligned with EN 16931
- Eliminate the need for prior approval by the European Commission to implement e-invoicing nationally
- Further accelerate the shift toward digitally native compliance systems
│ Implication: To comply, businesses must ensure that all invoiced entities are validated in real time — including their VAT status, legal identity, and registry status — ideally within the same invoicing workflow.
3. Platform Economy VAT Reforms
Under ViDA, digital platforms that facilitate short-term accommodation or passenger transport (e.g. Airbnb, Uber) will be deemed VAT suppliers in many B2C transactions. This reform:
- Shifts the burden of VAT collection and remittance to the platform
- Requires platforms to verify VAT numbers and business identities of service providers
- Brings uniform rules to cross-border digital services
│ Implication: Platforms will need robust, automated validation tools to assess the VAT status of their vendors and apply the correct tax treatment in real time.
4. Expanded OSS and IOSS Systems
ViDA also expands the One Stop Shop (OSS) and Import One Stop Shop (IOSS) to allow for simplified VAT registration across borders. Businesses will now be able to:
- Use a single VAT registration to report intra-EU B2C services
- Simplify reporting for own goods movement between warehouses
- Avoid registering for VAT in multiple EU states
│ Implication: Companies will increasingly need to manage and track multiple VAT numbers, linked to a single legal entity — a task made far easier with platforms like Global Database.
Understanding the Core ViDA Reforms
The VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) proposal, introduced by the European Commission, is designed to modernize how VAT is administered across the EU. It consists of three main pillars that will have far-reaching implications for how businesses validate, report, and manage VAT-related data:
1. Digital Reporting Requirements (DRR)
Starting from 2028, businesses engaged in intra-EU B2B transactions will be required to submit invoice data in near real-time to tax authorities. This replaces traditional VAT returns and introduces:
- A harmonized digital reporting format across EU member states
- Mandatory submission of structured electronic invoices within 2 days of issuance
- Increased scrutiny and reduced tolerance for errors in VAT numbers and entity data
│Implication: Businesses will need automated systems to validate VAT numbers before issuing invoices. Delays or mismatches will lead to reporting failures and financial exposure.
2. Mandatory E-Invoicing
ViDA will make e-invoicing the default method for cross-border B2B transactions within the EU. Unlike current systems where e-invoicing is optional or varies by country, the new rules will:
- Require structured invoice formats aligned with EN 16931
- Eliminate the need for prior approval by the European Commission to implement e-invoicing nationally
- Further accelerate the shift toward digitally native compliance systems
│Implication: To comply, businesses must ensure that all invoiced entities are validated in real time — including their VAT status, legal identity, and registry status — ideally within the same invoicing workflow.
3. Platform Economy VAT Reforms
Under ViDA, digital platforms that facilitate short-term accommodation or passenger transport (e.g. Airbnb, Uber) will be deemed VAT suppliers in many B2C transactions. This reform:
- Shifts the burden of VAT collection and remittance to the platform
- Requires platforms to verify VAT numbers and business identities of service providers
- Brings uniform rules to cross-border digital services
│Implication: Platforms will need robust, automated validation tools to assess the VAT status of their vendors and apply the correct tax treatment in real time.
4. Expanded OSS and IOSS Systems
ViDA also expands the One Stop Shop (OSS) and Import One Stop Shop (IOSS) to allow for simplified VAT registration across borders. Businesses will now be able to:
- Use a single VAT registration to report intra-EU B2C services
- Simplify reporting for own goods movement between warehouses
- Avoid registering for VAT in multiple EU states
│Implication: Companies will increasingly need to manage and track multiple VAT numbers, linked to a single legal entity.
The Hidden Risks of Invalid VAT Numbers

In the pre-ViDA era, an incorrect or outdated VAT number might have gone unnoticed—or at worst, caused a minor reporting delay. Under ViDA, however, the consequences of invalid VAT data become more immediate, more visible, and more costly.
Here are the key risks businesses face if they continue to rely on outdated, unverified, or incomplete VAT number records:
1. Rejected Invoices and Delayed Payments
Under the new digital reporting rules, invoices will be validated in near real-time by tax authorities. If a VAT number is missing, invalid, or doesn't match official registry data:
- The invoice can be rejected automatically
- The client may refuse to pay until corrections are made
- Delays could affect cash flow, supplier relationships, and compliance status
│With two-day reporting windows and growing automation in tax systems, businesses can no longer afford to send invoices without first validating the buyer’s and seller’s VAT numbers.
2. Tax Authority Audits and Fines
Increased automation doesn't mean reduced oversight—it means enhanced visibility for tax authorities. Any discrepancy between the submitted VAT number and the actual legal entity may:
- Trigger flags for investigation
- Result in fines or interest charges
- Damage your company’s compliance reputation
- Delay VAT refunds or input credit claims
│In some EU countries, invalid VAT numbers on a submitted invoice may render the transaction ineligible for VAT deductions.
3. Incorrect Tax Application and Liability
For platform operators, incorrectly identifying a supplier’s VAT status can lead to underpayment or overpayment of VAT—for which the platform may be held liable. This is especially critical when:
- A vendor claims to be VAT-registered but isn’t
- A buyer is treated as VAT-exempt without proper validation
- OSS/IOSS rules are applied incorrectly due to faulty tax IDs
│Even minor oversights can lead to platform-level liability, especially under the new ViDA provisions where the tax burden may shift to intermediaries.
4. Exposure to Fraud and Shell Companies
VAT fraud, including carousel fraud and phantom suppliers, thrives on unverified or poorly managed VAT data. Common risks include:
- Dealing with companies that no longer exist
- Receiving fake invoices from shell companies
- Overstating input VAT via fraudulent transactions
- Falling victim to scams that exploit mismatched or reused VAT numbers
│Without registry-level validation and ownership transparency, your business could be unknowingly exposed to criminal schemes and regulatory fallout.
🛡️ How Global Database Helps You Avoid These Risks
Global Database eliminates these risks by providing:
- Real-time VAT validation across 150+ countries
- Cross-checking of VAT numbers with official business registry data
- Full company enrichment: legal name, address, incorporation status, ownership, financials
- Audit logs to prove compliance at every step
- Continuous monitoring for changes in company or VAT status
How to Validate VAT Numbers in 150+ Countries
While ViDA focuses on reforming VAT systems within the European Union, many businesses operate in a global context—selling to or sourcing from partners around the world. That means compliance workflows must go beyond the EU and include VAT, EIN, CNPJ, GSTIN, and other tax identifiers used globally.
Yet, verifying tax IDs across jurisdictions is far from simple. Each country has its own formats, registries, update cycles, and data availability. Relying on local tax authority websites, spreadsheets, or public portals like VIES introduces inconsistency and limits automation.
Global Database solves this by offering one unified platform to validate business tax identifiers across 150+ countries — all from official government sources.
✅ What You Can Validate with Global Database
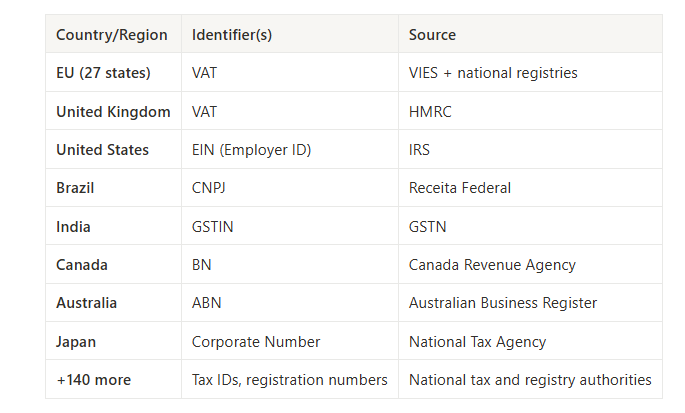
Every identifier is checked against first-party government data, ensuring unmatched reliability and legal defensibility in audit scenarios.
🔄 Real-Time Validation via API or Web
You can validate VAT and tax numbers in three ways with Global Database:
- Web-based Search – Validate a single business via our online portal
- Bulk Upload – Upload spreadsheets of entities and receive verified/enriched results
- RESTful API Integration – Automate validation in your CRM, ERP, onboarding, or invoicing systems
Each method returns not just a “valid/invalid” result, but also enriched company data such as:
- Legal name and entity type
- Registered address
- Incorporation status
- Industry classification
- Ownership and group structure
- Financial metrics (where available)
🧠 Why a Unified Validation System Matters
Without centralized, standardized validation, teams risk:
- Conflicting results across jurisdictions
- Inconsistent due diligence
- Delays in onboarding or invoicing
- Errors in tax treatment or platform liability
Global Database removes this friction by normalizing global tax data, so you can validate and enrich any business identity — regardless of country — with one simple query.
🔐 ViDA + Global Tax Coverage = Future-Proof Compliance
While ViDA is EU-specific, it reflects a global trend toward real-time digital tax enforcement. Countries in Latin America, Asia, and the Middle East are also introducing e-invoicing mandates and tighter ID requirements.
By partnering with Global Database, you prepare not only for ViDA, but for the next wave of global tax digitization.
Building a ViDA-Ready Validation Workflow with Global Database
Preparing for ViDA isn't just about validating a few VAT numbers — it’s about transforming VAT number validation into a fully integrated, automated, and auditable process. To stay compliant under ViDA’s real-time digital reporting and e-invoicing requirements, businesses need to embed validation into their core operations — from onboarding and invoicing to ongoing compliance monitoring.
Here’s how to build a ViDA-ready workflow using Global Database:
1. Automate Validation at Every Entry Point
Whether it’s a new supplier, a customer checkout, or a new record in your CRM — the moment a VAT number enters your system, it should be verified.
With Global Database’s real-time API, you can automatically check:
- The validity of the VAT or tax ID
- That it matches the correct legal entity
- That the entity is active and properly registered
│📌 Use Case: Validate suppliers during onboarding to prevent registration issues and fraud exposure before they happen.
2. Enrich Records with Full Company Profiles
A VAT number alone isn’t enough in a ViDA environment. Tax authorities will expect consistency across:
- Registered name and address
- Incorporation status
- Legal form
- Cross-border operations (OSS/IOSS)
Global Database delivers full company profiles tied to each tax ID — including ownership structure, registration number, financials, and more — all sourced from official government registries.
│📌 Use Case: Enrich CRM records for buyers and suppliers with accurate registry data for audit-readiness.
3. Support Structured E-Invoicing Requirements
ViDA requires invoices to follow structured formats (e.g., EN 16931 XML), which means the data behind your invoice must be machine-readable and compliant.
By validating and enriching VAT numbers before invoice generation, Global Database ensures:
- Your invoices are accepted by tax authorities
- Buyer and seller details are correct and verifiable
- The right tax treatment is applied (domestic, reverse charge, OSS, etc.)
│📌 Use Case: Integrate validation into your accounting software or e-invoicing platform to preempt rejections and accelerate processing.
4. Monitor for Changes and Maintain Compliance
A company’s VAT status, ownership, or legal form can change — especially in high-volume or cross-border operations. ViDA’s real-time reporting requirements make ongoing monitoring essential.
Global Database enables continuous tracking of:
- VAT status changes (e.g. deregistration, suspension)
- Company status updates (e.g. liquidation, address change)
- Risk indicators (e.g. credit score drops, adverse filings)
│📌 Use Case: Schedule recurring validation checks for high-risk vendors or all parties above a certain transaction value.
5. Create an Audit-Ready Trail
ViDA mandates fast reporting and increases the likelihood of audits. You need clear proof that:
- You validated a VAT number
- The data was correct at the time of invoicing
- You applied the right tax logic
Global Database logs every query and provides timestamped verification records for full traceability.
│📌 Use Case: Export validation logs for your accounting team or tax advisor in the event of a VAT review.
Why Enriched Data Beats Basic VAT Checks
In a ViDA-regulated environment, validating whether a VAT number is simply “active” is no longer sufficient. Businesses need to go beyond yes/no validation and gain a full picture of the entity behind that number — especially when dealing with cross-border transactions, high-risk suppliers, or platform-based vendors.
This is where enriched VAT data becomes essential.
✅ What Is Enriched VAT Validation?
Basic VAT validation tools (like the VIES portal) return minimal information:
- Whether the VAT number is valid
- Sometimes the associated company name and country
- Often no response at all if the system is overloaded or the member state doesn't return data
Enriched validation, on the other hand, provides comprehensive, registry-linked insights such as:
- Legal entity name
- Registered address
- Company registration number
- Business status (active, dissolved, suspended)
- Date of incorporation
- Legal form and industry classification
- Ownership structure and group hierarchy
- Company financials (where available)
📉 The Risks of Relying on Basic Validation Alone
When you rely on minimal or outdated information:
- You risk applying incorrect VAT treatments
- You may onboard inactive or shell companies
- You open yourself to fraud, audit flags, and compliance gaps
- You lack sufficient documentation for tax authority reviews
And if your teams are manually validating VAT numbers across VIES, local websites, or spreadsheets, you're wasting time and increasing the likelihood of human error.
💡 How Global Database Adds Strategic Value
Global Database enhances your VAT validation process by delivering:
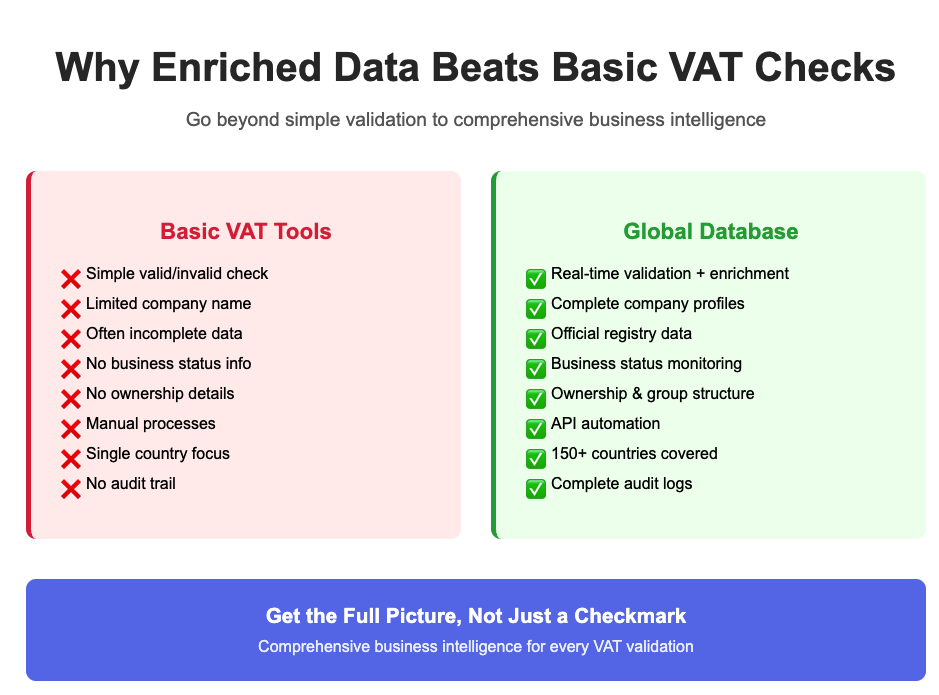
With enriched data, your VAT validation process doesn’t just meet ViDA requirements — it helps you streamline onboarding, reduce fraud, and support broader compliance goals like KYB, AML, and platform liability management.
🔄 Use Cases for Enriched VAT Validation
- Supplier Onboarding: Ensure suppliers are real, active, and properly registered
- Invoicing: Auto-fill buyer details based on VAT number with verified data
- Risk Management: Flag high-risk entities using status, financials, or group links
- CRM & ERP Sync: Keep all records clean, complete, and compliant
- Platform Seller Checks: Identify undeclared or misclassified vendors
Why Leading Platforms and Enterprises Trust Global Database
As compliance standards rise across the EU and beyond, businesses are recognizing that VAT validation must evolve into a strategic function — not just a finance task. That’s why a growing number of marketplaces, financial institutions, ERPs, trade platforms, and compliance teams rely on Global Database to support their operations.
Our platform goes far beyond traditional VAT checkers or public portals by offering an end-to-end solution for validation, enrichment, and integration — tailored for companies operating at scale.
🚀 Trusted by Market Leaders
Global Database powers real-time business verification and tax ID validation for some of the most demanding organizations, including:
- Sales platforms and CRM providers validating customer and vendor data across borders
- Financial institutions managing KYB, credit risk, and compliance workflows
- E-invoicing and tax tech companies ensuring every invoice sent is VAT-compliant
- Government agencies and procurement platforms needing auditable identity checks
What these companies have in common is the need for global coverage, first-party data accuracy, and seamless automation — all delivered by Global Database.
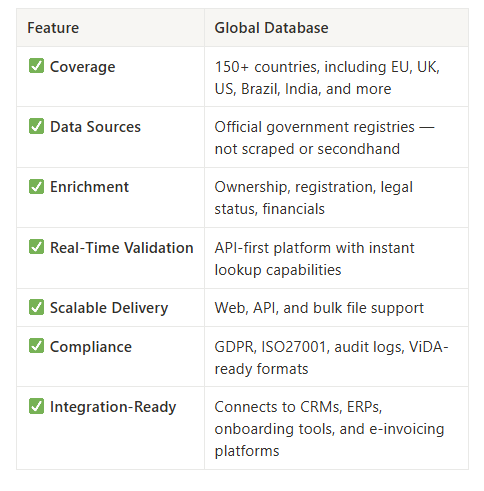
🌍 What Sets Us Apart
Here’s why our clients choose Global Database as their ViDA compliance partner:

Scenarios Where We Deliver the Most Value
- High-volume marketplaces onboarding thousands of sellers across jurisdictions
- Cross-border e-commerce businesses that need correct VAT treatment instantly
- RegTech and FinTech platforms embedding KYB into their onboarding flow
- Procurement teams ensuring supplier legitimacy before contract execution
- Accounts payable/receivable teams needing accurate invoicing workflows under ViDA
Conclusion: Get Ahead of ViDA Before It’s Too Late
The VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) package is not just a regulatory update — it’s a full-scale transformation of how tax compliance will function across the European Union. With mandatory e-invoicing, real-time reporting, and increased VAT liability for platforms, the margin for error is shrinking fast.
Manual validation, partial datasets, and legacy tools like VIES will no longer meet the needs of modern, cross-border businesses. Instead, companies must adopt solutions that deliver accuracy, automation, and audit-readiness — all backed by official registry data.
🎯 Key Takeaways:
- ViDA will require real-time validation of VAT numbers and structured invoice reporting
- Inaccurate or outdated VAT information will result in rejected invoices, fines, or audit flags
- Businesses must validate more than just a number — ownership, registration, and legal status now matter
- Relying solely on public portals or manual workflows is no longer viable
- Global Database offers a unified, scalable, and ViDA-compliant solution for VAT and tax ID validation across 150+ countries
🔍 Is Your Business ViDA-Ready?
Use this quick checklist to assess your current process:
✅ Can you validate VAT numbers in real time — across all EU countries?
✅ Are you able to enrich those records with verified company data (e.g. ownership, address, status)?
✅ Can your invoicing or onboarding process automatically check tax IDs at scale?
✅ Do you have an audit trail proving you verified each tax ID before use?
✅ Can you support structured e-invoicing flows under EN 16931 or DRR standards?
If you answered “no” to any of these, now is the time to take action.
🚀 How to Get Started
Global Database is ready to help you prepare for ViDA with:
- Real-time VAT and tax ID validation
- Coverage in 150+ countries
- Seamless API and bulk integration
- Enriched company profiles from official registries
- Audit-ready documentation and continuous monitoring
👉 [Try Free VAT Validation]
👉 [Request API Access]
👉 [Book a Compliance Demo]
Final Thought
ViDA represents a new era of digital VAT compliance — one that rewards businesses that invest early in data quality, automation, and transparency.
With Global Database, you gain more than a validation tool — you gain a long-term compliance partner that helps you stay ahead of regulation, fraud, and operational risk.
